 Since 2001, April has been the National Sexual Violence Resource Center’s Sexual Assault Awareness Month. The main goals of Sexual Assault Awareness Month are to raise awareness about sexual assaults and share information about how to help prevent it through education. It is also a time for communities to communicate with advocates, survivors, and their loved ones to increase knowledge, awareness, and identify resources and strategies to reduce sexual violence.
Since 2001, April has been the National Sexual Violence Resource Center’s Sexual Assault Awareness Month. The main goals of Sexual Assault Awareness Month are to raise awareness about sexual assaults and share information about how to help prevent it through education. It is also a time for communities to communicate with advocates, survivors, and their loved ones to increase knowledge, awareness, and identify resources and strategies to reduce sexual violence.
Organizations such as the Joyful Heart Foundation have been formed with a mission to transform society’s response to sexual assault, domestic violence, and child abuse, and provide support to survivors. In honor of Sexual Assault Awareness month, we’ll explore the role accredited forensic testing plays in solving violent crimes and getting justice for victims of sexual assault.
The National Sexual Assault Kit Initiative was established in 2015 by the Bureau of Justice Assistance (BJA) to improve the criminal justice response to sexual assault and safeguard justice for victims. This is accomplished by aiding in the investigation and prosecution of cases, employing a comprehensive and victim-centered approach, and enhancing jurisdictional capacity to prevent the accumulation of unsubmitted sexual assault kits in the future.
According to an investigation conducted by CBS News in 2009, over 20,000 sexual assault kits were not submitted to crime laboratories for testing in 24 cities and states including Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, California, Connecticut, Florida, Illinois, and Indiana. The National Institute of Justice unveiled nationwide survey results regarding forensic evidence not submitted by law enforcement agencies to crime labs:
- 18% were unsolved rapes
- 14% were unsolved homicides
- 23% were unsolved property crimes
Results also revealed the following reasons why the law enforcement agencies who responded to the survey did not submit forensic evidence to the crime labs:
- Suspect was not identified
- Analysis was not requested by the prosecutor
- Uncertainty of usefulness
These reports put the number of untested sexual assault kits under the microscope nation-wide and the public demanded action. For example, it was reported that in Detroit 10,500 untested sexual assault kits from 1988 to 2006 were found in police storage.
Since the establishment of the National Sexual Assault Kit Initiative, over 245,000 sexual assault kits have been inventoried, and more than 101,000 have been sent for testing thereby resulting in over 19,000 CODIS hits based on state and local level reports.
With that being said, has the United States made any progress in the sexual assault kit backlog?
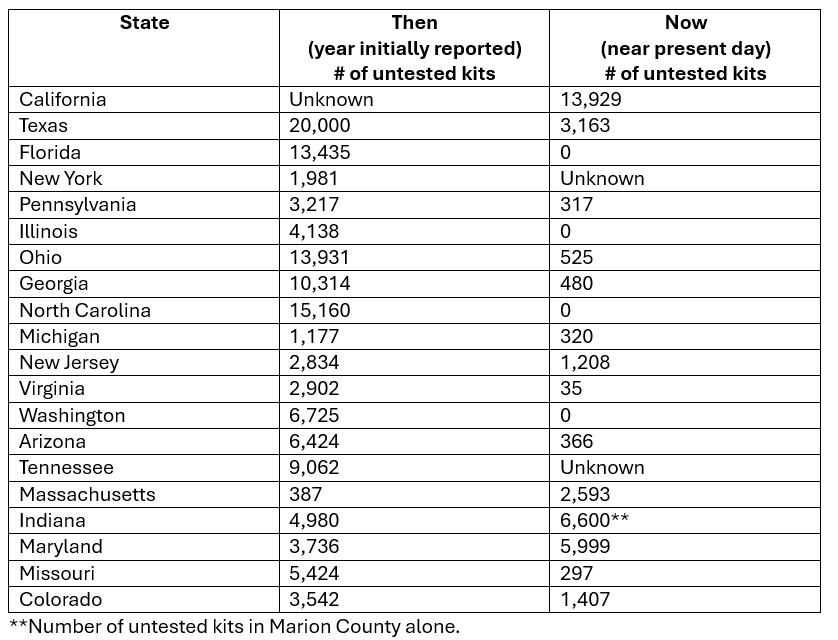
Notes: Number of untested sexual assault kits were obtained from End the Backlog. Ranked top 20 most populated states in the U.S. were based on World Population Review.
Those involved in the Sexual Assault Kit Initiative, including the law enforcement agencies submitting the kits, the forensic science service practitioners processing the kits, and the criminal justice system, have worked diligently on this incredible challenge.
To accomplish the goals of the initiative, many issues had to be addressed. For instance, law enforcement agencies had to improve training regarding evidence collection, prioritization of the submission of sexual assault kits to the lab for analysis, and communication with the prosecutors about what was needed to build a case. In addition, prosecutors had to improve training on case management and cold cases and familiarize themselves with crime laboratory techniques and forensic evidence for trial.
To keep up with the high demand, crime laboratories implemented high-throughput analysis procedures including robotics and automation such as Qiagen EZ2 Connect for automated isolation of nucleic acids from up to 24 samples; QIAgility for automated PCR setup; and Applied Biosystems 3500 Series Genetic Analyzer with up to 24 capillaries.
During this transition, laboratories had to ensure that all methods and instrumentation were validated in accordance with international standards, quality assurance standards, and supplemental accreditation requirements. Some crime laboratories were already operating at full capacity; therefore, they had to resort to outsourcing. If outsourcing is used, it is crucial that the vendor laboratory utilized is compliant with the following accreditation and quality assurance standards so that the DNA profiles generated by the vendor laboratory are eligible for CODIS entry:
- Compliance with FBI Quality Assurance Standards for Forensic DNA Testing Laboratories
- Accreditation by an approved accrediting body such as A2LA
A2LA offers a Forensic Examination Accreditation Program for forensic testing organizations to ensure a robust system of quality assurance, earn public trust, and confirm compliance with regulatory and statutory requirements. In 2014, the National DNA Index System (NDIS) Procedures Board approved A2LA as an accrediting agency under the United States Federal DNA Identification Act. Through A2LA’s Forensic Examination Accreditation Program, laboratories performing DNA analyses on DNA samples for CODIS entry purposes and laboratories performing DNA analyses on known or casework reference samples can be assessed to the FBI Quality Assurance Standards for Forensic DNA Testing and/or DNA Databasing Laboratories and ISO/IEC 17025.
In addition, A2LA has been identified by the Texas Forensic Science Commission as an accrediting body to assess laboratories performing forensic analysis of physical evidence for use in criminal proceedings in accordance with the Texas Administrative Code. Furthermore, The Maryland Department of Health and Mental Hygiene and the Office of Health Care Quality recognizes A2LA as a deemed accreditation body under the State of Maryland in accordance with the Code of Maryland Regulations.
To help forensic crime labs across the country pay for additional staff and equipment, the BJA’s Formula DNA Capacity Enhancement for Backlog Reduction (CEBR), a grant program, has become available. The overall objective of this program is to increase the number of forensic DNA and DNA database samples being processed for CODIS entry which will help solve crimes. Some states have become creative in their effort to help finance the analysis of the sexual assault kits. For instance, proceeds from the “pole tax” in Texas are used to support programs combating sexual assault.
To achieve the victim-centered approach in the Sexual Assault Kit Initiative, states like Idaho have implemented a statewide sexual assault evidence kit tracking system which provides the public accountability and transparency. Survivors of sexual assaults are given a tracking number at the time of collection and they can view the history and status of their sexual assault kit. It is important to note that this tracking system (Idaho Sexual Assault Kit Tracking System) is not considered an official chain of custody record for legal purposes.
In addition to implementing a tracking system, Idaho State Police Forensic Services has trained over 261 nurses in their International Association of Forensic Nurses (IAFN) certified 40-hour course, Adult/Adolescent 40-hour SANE Course, which aligns with the IAFN SANE Education Guidelines. The Idaho State Police Forensic Services is actively educating nurses, law enforcement, and Idaho citizens about the important role forensic nursing plays in the criminal justice system.
The Georgia Criminal Justice Coordinating Council (CJCC) created a multidisciplinary review team comprising of law enforcement representatives, sexual assault nurse examiners, prosecutors, the Georgia Bureau of Investigation Crime Laboratory, sexual assault centers, and the Sexual Assault Unit at CJCC. In 2022, CJCC successfully implemented the Forensic Advantage SAK Tracking System at full operational capacity across all 159 counties in the State of Georgia. It’s important to recognize that Georgia’s criminal justice system consists of approximately 800 agencies, and each agency manages sexual assault kits at various stages of processing; therefore, there was a necessity for a tracking system to improve the efficiency. A key benefit to utilizing Forensic Advantages SAK Tracking System is that it allows survivors to securely monitor the kit status. In addition, the laboratories can track the number of kits submitted, provide detailed statistics, and ensure accountability.
As illustrated in Table 1, our nation has come a long way but has a long way to go still. Let’s keep the momentum going!
Take the first step in building quality and confidence in your organization. Click here to request an estimate. For more information about accreditation, contact A2LA at info@A2LA.org, or give us a call at 301.644.3248.
References:
National Sexual Violence Resource Center: https://www.nsvrc.org/saam/history
Administration For Children and Families: https://acf.gov
Joyful Heart Foundation: https://www.joyfulheartfoundation.org/
End The Backlog: https://www.endthebacklog.org/#explore_backlog_map
Sexual Assault Kit Initiative: https://www.sakitta.org/
Qiagen: https://www.qiagen.com/
Thermo Fisher Scientific: https://www.thermofisher.com/
Smith, M. (2011). High Court Approves “Pole Tax” on Strip Clubs. The Texas Tribune. https://www.texastribune.org/2011/08/26/high-court-approves-pole-tax-strip-clubs/
Bureau of Justice Assistance. (2024). DNA Funding for Forensics Labs Easing Case Backlogs. https://bja.ojp.gov/news/blog/dna-funding-forensics-labs-eases-case-backlogs
Idaho Sexual Assault Kit Tracking: https://apps.isp.idaho.gov/SexualAssaultKitTracking/
Forensic Advantage. (2024). Streamlining Justice with Forensic Advantage SAK Tracking System. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/streamlining-justice-forensic-advantage-sak-m2b8c/
Forensic Advantage Systems: https://www.forensicadvantage.com/sexual-assault-kit-tracking-system
International Association of Forensic Nurses: https://www.forensicnurses.org/
A2LA – Forensic Examination Accreditation Program: https://a2la.org/accreditation/forensics/
